Special education serves a diverse population of students with disabilities—cognitive, physical, emotional, and learning challenges. Traditional education systems, built for uniformity, often fail to provide the tailored support these students need, resulting in gaps in engagement, comprehension, and inclusion.
Enter Generative AI (Gen AI): a transformative technology reshaping the educational landscape. With the ability to personalize learning, enhance accessibility, and support emotional well-being, Gen AI equips educators with tools to address individual needs at scale—offering students with disabilities more equitable opportunities to thrive.
Recent studies highlight this potential. According to UNESCO, AI in education has shown promising results in increasing engagement and academic outcomes for students with diverse needs. As these technologies become more accessible, their integration in special education is poised to expand rapidly.
1: Understanding Gen AI and Special Education
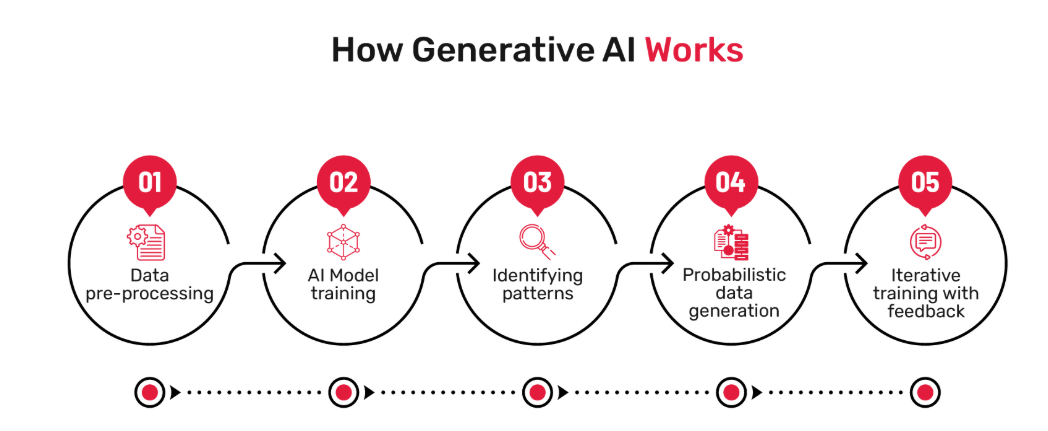
Source: What is the Future of Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to algorithms capable of producing text, images, audio, and other outputs based on learned data patterns. Tools like ChatGPT, DALL·E, and Synthesia exemplify Gen AI in action, generating content tailored to the user’s needs.
Students in special education may face a wide range of needs:
- Learning disabilities (e.g., dyslexia, dyscalculia)
- Cognitive impairments
- Speech or communication difficulties
- Physical disabilities
- Emotional and behavioral disorders
Most mainstream curricula rely on one-size-fits-all models, limiting flexibility and personalization. Teachers often lack sufficient time and resources to adapt content for each student. Gen AI offers scalable solutions that can:
- Customize materials instantly
- Adjust pacing in real time
- Provide alternative content formats
A study by the National Center for Learning Disabilities found that adaptive technologies significantly improved learning outcomes for students with dyslexia and other reading difficulties.
2: Key Benefits of Gen AI in Special Education
Personalized Learning Paths
Adaptive platforms like Squirrel AI and Khanmigo create dynamic learning experiences. They adjust content difficulty, presentation style, and pacing based on student performance—helping ensure every learner progresses at their optimal pace.
Improved Accessibility
Gen AI enhances accessibility through:
- Auto-generated transcripts and audio descriptions
- Braille and large-print content
- Simplified summaries for cognitive delays
Tools like Microsoft Immersive Reader and Be My Eyes empower visually impaired and neurodiverse learners to engage with content independently.
Communication Assistance
Non-verbal students benefit from:
- Symbol-based communication tools (e.g., Avaz AAC)
- Speech-to-text and text-to-speech features
These tools promote greater independence and active participation in classroom interactions.
Emotional and Behavioral Support
AI-driven tools support emotional well-being:
- Chatbots like Woebot guide students in managing emotions and stress.
- Predictive analytics alert educators to early signs of distress, enabling timely interventions.
A study in JMIR Mental Health found chatbots like Woebot effective in reducing anxiety symptoms among young users.
Automated Content Generation
Educators can quickly create:
- Simplified texts and instructional visuals
- Interactive exercises tailored to varied learning needs
Platforms like Qolaba enable teachers to generate differentiated materials on demand, reducing prep time while enhancing instructional quality.
Real-Time Feedback & Assessment
AI-powered systems offer instant feedback and adaptive guidance. For example, DreamBox adjusts math problems in real time based on student input, keeping learners engaged and appropriately challenged.
3: Applications of Gen AI in Special Education
AI Tutors & Virtual Assistants
Tools like Magic School AI and ChatGPT provide 24/7 personalized support. They allow students to revisit concepts at their own pace, with AI adjusting explanations to match comprehension levels.
Adaptive Learning Platforms
Platforms such as DreamBox and ChatGPT-integrated systems modify content in real time, scaffold lessons, and bridge learning gaps—especially helpful for students needing reinforcement in core subjects.
Augmentative & Alternative Communication (AAC) Tools
Apps like Avaz AAC enhance communication by suggesting expressive language options and predicting contextually relevant words, enabling non-verbal students to engage more fully.
Predictive Analytics
AI dashboards empower educators to monitor engagement and identify potential learning challenges early. Adjustments in instructional strategies can then be tailored to each student’s evolving needs.
Immersive Learning (AR/VR + AI)
Immersive environments like Tilt Brush and AI-powered VR scenarios provide engaging, multisensory experiences. These tools are particularly valuable for students with attention disorders or autism, fostering creative exploration and deeper engagement.
4: Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Data Privacy & Consent
Special education involves handling sensitive information about minors and their unique needs. Educators and developers must strictly comply with data privacy regulations such as FERPA and GDPR. Clear, transparent communication with parents or guardians is crucial to secure informed consent for any data use. Additionally, data storage and sharing practices must prioritize encryption and limited access to safeguard student privacy.
Ensuring Human Oversight
AI should serve as an assistive tool, not a replacement for human educators, therapists, or caregivers. While AI can automate tasks like content generation or provide real-time feedback, it lacks the emotional intelligence and cultural understanding required to nurture holistic growth. Teachers and caregivers must remain actively involved to interpret AI outputs, provide empathy-driven support, and maintain the human connections essential in special education settings.
Balanced AI Use
There is a risk of overdependence on AI tools, potentially limiting opportunities for social interaction and critical thinking. To mitigate this, schools should adopt hybrid instructional models. AI can handle routine and individualized tasks, freeing educators to focus on fostering collaboration, discussion, and creativity among students. Establishing clear guidelines on when and how AI is used ensures it enhances—rather than dominates—the learning experience.
5: The Future of Gen AI in Inclusive Education
Emerging Innovations
AI innovations are rapidly evolving. Multimodal AI systems capable of processing and combining voice, text, and visual inputs will enable more immersive, adaptable learning experiences. Emotion-aware AI will soon allow educators to receive real-time insights into student engagement and emotional states, helping them proactively adjust instructional strategies to maintain motivation and well-being.
Collaborative Potential
Effective use of Gen AI in special education hinges on collaboration across multiple stakeholders. Teachers, administrators, AI developers, caregivers, and students themselves must work together to design and refine AI tools that genuinely address classroom needs. Regular feedback loops and inclusive design practices ensure that AI solutions respect diverse learning styles and cultural contexts.
Vision for Inclusive Classrooms
The ultimate goal is to create classrooms where every student—regardless of disability—can access learning materials tailored to their needs and pace. Imagine an environment where a non-verbal student uses an AAC device to participate in class discussions, while an adaptive platform adjusts math challenges in real time for another learner. With Gen AI’s ongoing advancements, this vision of a fully inclusive, personalized educational experience is increasingly within reach.
Conclusion
Generative AI is transforming special education—not by replacing teachers, but by amplifying their ability to deliver personalized, inclusive, and compassionate learning. From adaptive learning paths to accessibility and emotional support, AI is helping create more equitable educational experiences for students with disabilities.
Thoughtful implementation is key. AI must be used ethically, with strong human oversight and data protections. As innovation continues, collaborative efforts across schools, families, and technology partners will be critical in realizing Gen AI’s full potential.
When used well, Gen AI can help foster classrooms where every student—regardless of ability—can learn, grow, and thrive.
FAQs
1. How does Gen AI personalize learning for students with disabilities?
By analyzing student data and behavior, Gen AI adapts content type, difficulty, and pace to individual needs.
2. Can Gen AI replace special education teachers?
No. It supports teachers by automating repetitive tasks and offering additional tools but cannot replace human interaction, empathy, or judgment.
3. What are some examples of Gen AI tools for special education?
DreamBox, ChatGPT, Avaz AAC, Microsoft Immersive Reader, Woebot, Qolaba, Magic School AI.
4. Is Gen AI accessible to all students, regardless of disability?
It can be, but accessibility depends on thoughtful design. Developers must ensure compatibility with assistive technologies and address diverse learning needs.5. Is it safe to use Gen AI with children and teens in special education settings? When used with proper data protections, parental consent, and educator oversight, Gen AI can be safely integrated into special education.





